Skin Texture
Larges Pores
The buildup of dead skin cells and keratin on the skin’s surface leads to thicker, rougher skin texture and enlarged pores. This accumulation obstructs the absorption of water and nutrients, resulting in dullness and dryness. Increased sebum production exacerbates the appearance of enlarged pores.
Broadly speaking, enlarged pores may stem from factors such as excessive sebum production, aging, prolonged sun exposure, genetic predisposition, gender, age, skin irritation, acne, and conditions like seborrheic dermatitis. Genetics also play a significant role in determining pore size.
Cause
- High Sebum Secretion
- Aging
- Enlarged Hair Follicles
- Long-term drinkers and smokers
- Inadequate Sun Protection
- Clogged Pores
- Squeezing acne or pores can irritate the skin and increase sebum production.
- Elevated levels of androgens, such as those with diabetes.
- Neglect proper makeup removal or facial cleansing routines
- Using low-quality skincare products.
- lacking a consistent daily facial care regimen.
- Unhealthy lifestyles or diets, such as staying up late, consuming high-fat or high-sugar foods, or indulging in spicy foods.
Symptoms
Skin with enlarged pores often appears uneven and rough in texture. Large pores can be classified into four main types: keratin-related, oily skin-related, dry skin-related, and age-related.
- Keratin Skin Type Enlarged Pores:
When excess keratin accumulates, it can block pores, leading to the formation of blackheads and whiteheads. Blackheads manifest as small black dots, while whiteheads appear as small white bumps around the pores. - Oily Skin Type Enlarged Pores:
Excessive sebum production can cause pores to appear larger and oilier, particularly in the T-zone (forehead and nose). This can result in a greasy complexion with yellowish, dull skin and U-shaped enlarged pores. - Dry Skin Type Enlarged Pores:
Pores may take on an oval shape in individuals with dry or dehydrated skin, exacerbated by factors like long-haul flights that can further dry out the skin. Dry skin tends to exhibit more textural irregularities compared to other skin types. - Aging Skin Type Enlarged Pores:
With aging, pores may adopt a Y-shaped or water droplet shape due to the loss of collagen and skin elasticity. This weakening of support structures around the pores can cause adjacent pores to collapse together, forming lines or patterns.
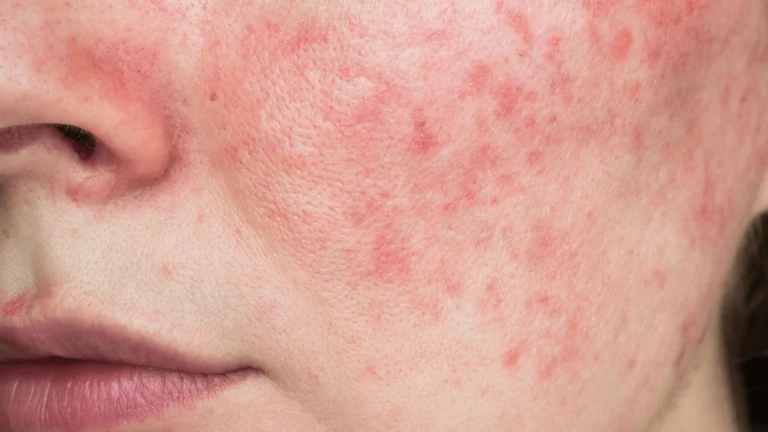
Facial Redness/Capillary Vessels
Facial redness, medically termed telangiectasias, is characterized by the presence of visible capillary vessels on the skin’s surface. When the skin becomes irritated, capillary vessels expand, becoming visible through the skin. While temporary blushing may occur due to this dilation, repeated episodes can lead to persistent facial redness, known as erythema.
Causes
Skin redness and visible capillary vessels are primarily attributed to a thin stratum corneum, offering less protection and leaving capillaries closer to the skin surface, thus more susceptible to external factors.
- Genetic Predisposition
- Sensitive Skin
- Prolonged Sun Exposure
- Weak or Damaged Skin Barrier
- Unhealthy Diet:
Symptoms
Individuals with visible facial capillaries typically exhibit a consistently red skin tone, particularly pronounced on the cheeks and nose wings, often appearing symmetrical. This redness is indicative of a chronic redness condition, associated with a thin stratum corneum and heightened skin sensitivity. Emotional fluctuations or extreme temperatures can intensify the redness, and those with severe facial redness may develop hyperpigmentation.
The redness contributes to a dull and rough skin texture. Due to the skin’s reduced tolerance to irritants, it becomes fragile and sensitive, prone to itching, redness, and other skin reactions upon exposure to triggers. These reactions often persist for an extended period and take longer to heal.
Sensitive Skin / Impaired Skin Barrier
If you frequently experience flakiness, itching, redness, or acne on your face throughout the year, you might have a compromised skin barrier or sensitive skin. Research indicates that 30-40% of people have sensitive skin, often linked with barrier damage.
Sensitive skin represents a state of suboptimal skin health, falling between a healthy and unhealthy condition. It arises from intricate processes involving the skin barrier, nerves, blood vessels, immunity, and inflammation. When exposed to external irritants, the skin may react in various ways, such as erythema, papules, spider veins (telangiectasia), tingling or burning sensations, and increased sensitivity to regular cosmetics. This condition is termed sensitive skin. Notably, a compromised skin barrier is closely linked to the development of sensitive skin.
To simplify, the skin barrier acts as a protective shield composed of sebum and the stratum corneum.
Sebum Barrier: The sebum barrier is a protective layer formed by a combination of sebum secreted by sebaceous glands, lipids from keratin breakdown, and sweat. It consists of triglycerides, wax esters, squalene, and cholesterol.
Stratum Corneum: This layer is often described as a “bricks and mortar” structure, composed of corneocytes (the “bricks”) surrounded by intercellular lipids (the “mortar”). The intercellular lipid matrix includes ceramides, free fatty acids, and cholesterol.
The stratum corneum acts as a protective barrier, akin to a brick wall, with corneocytes supported by intercellular lipids. The integrity of both the stratum corneum and sebum barrier is vital for skin health.
A robust skin barrier effectively shields against external irritants, UV radiation, and prevents transepidermal water loss. It also plays a role in anti-inflammatory processes, contributing to overall skin resilience and health.
Causes
The majority of skin barrier damage is attributed to human actions, rather than being inherent at birth. However, sensitive skin can arise from both external factors and natural predispositions.
- Aggressive Products
- Overwashing or Harsh Exfoliation
- Individuals with skin disorders like rosacea, hormone-dependent dermatitis, or lupus erythematosus
- External factors such as extreme temperatures, UV radiation, or air pollution can compromise the skin barrier
Symptoms
- Sensations of tightness, tingling, burning, or itching is common.
- Thinning of the stratum corneum, leading to increased susceptibility to allergic reactions and redness.
- Skin exhibits heightened sensitivity, often resulting in flushing or redness, particularly in response to temperature fluctuations.
- Skin appears flaky, dry, and struggles to retain moisture, even with the application of moisturizers.
- Frequent occurrence of closed comedones (whiteheads) in localized areas, with recurrence after treatment.
- Prone to allergic reactions, even to mild stimuli.
- Persistent skin inflammation contributes to a fatigued appearance.
Dry and Flaky Skin
Is your skin feeling as parched as the desert sands? Despite layering on moisturizer after moisturizer, does your makeup still refuse to cooperate, leaving your skin looking flaky or scaly? Our skin’s outermost layer serves as a natural barrier, shielding us from environmental aggressors while regulating our skin’s hydration levels. However, maintaining a healthy skin barrier isn’t always a given. Factors like age, lifestyle choices, skincare habits, and exposure to external irritants can compromise its integrity. As a result, the skin barrier may lose its ability to retain moisture in the stratum corneum. When water content in this layer drops below 10%, it often leads to dry, rough, cracked, and flaky skin—a common concern, especially for individuals with dry skin types.
Causes
- Genetic predisposition
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Dehydration
- Aging
- Compromised skin barrier
- Dry and harsh weather conditions
- Inflammatory skin conditions or diseases
Symptoms
dehydrated skin include a lackluster complexion, tightness, cracking, fine lines, and flaky patches. Additionally, individuals may experience heightened sensitivity and a tingling sensation on the skin.
Overproduction of Sebum on the Skin
Excess sebum, or oil, originates from sebaceous glands situated in the dermis. These glands naturally produce sebum to lubricate and shield the skin’s surface. However, when these glands become hyperactive, they generate an abundance of sebum, resulting in oily skin.
Oily skin often arises from skin dehydration, creating an imbalance between oil and water levels. This imbalance triggers the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum as a protective response against further moisture loss. Thus, the correlation between sebum production and skin hydration is vital to understand, affecting individuals with dry or oily skin types alike.
Causes
- Dry or Dehydrated Skin
- Naturally oily or combination skin
- Hormonal Imbalance
- Sensitive Skin with Barrier Damage
- Dietary Factors
- Inadequate Skincare Routine
- Poor Hygiene Practices
- Prolonged Computer Use
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with overactive sebaceous glands include excessively oily skin, dry patches, lackluster complexion, enlarged pores, whiteheads, blackheads, and compromised skin barrier.
Dark/Yellowish Skin Tone
Skin tone is determined by the presence of melanin molecules in the skin, with higher melanin levels resulting in darker skin tones. Various factors such as exposure to UV light, dietary habits, stress levels, genetics, and physiological factors can influence melanin production. Additionally, individuals with lighter skin tones may still have underlying tones, often appearing slightly yellowish in complexion.
Causes
- Genetics
- Sun Exposure
- Dietary Factors
- Skin Dehydration
- Aging
- Sleep Patterns
Symptoms
Dark, yellowish skin often appears dull and lacks radiance, affecting one’s overall complexion. Opting for skin lightening treatments can help address this issue, although individual results may vary due to genetic factors. A simple way to gauge potential results is by examining the skin on the inner upper arms, which can provide insight into the achievable degree of skin lightening.
Dull Skin
Dull skin is often associated with the natural aging of the skin. As we age, our skin gradually loses its luminosity and its capacity to reflect light effectively. It’s essential to distinguish dullness from other skin conditions like tanning or yellowish undertones, as dullness primarily refers to the lack of radiance and presence of hyperpigmentation.
- Dehydration and dryness in the skin’s outer layer, or epidermis, can lead to dullness.
- Skin oxidation, Excessive exposure to factors like prolonged computer or mobile phone use, late nights, and emotional stress can trigger oxidation, leading to the accumulation of free radicals in the skin.
- Sun exposure without adequate protection can accelerate the development of hyperpigmentation
- Irregular epidermal renewal can lead to the accumulation of old skin cells, which can clog hair follicles and contribute to uneven skin texture.
- Diminished oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood can impact the skin’s vitality.
- Individuals prone to allergies may experience dull skin and dark circles under the eyes.
Symptoms
Yellowish skin tone ≠ dull skin tone
Dull skin is characterized by:
- Rough or uneven texture
- Lack of natural radiance
- Uneven pigmentation or skin tone
A:TriFX Radiofrequency (RF) Microneedling:
B:SmoothGlo™
C:M22 IPL
D:Acid Peeling
E:Mesotherapy
F:Herbal formulas: aimed at toning the body’s health and beauty from the inside out.
The first step in anti-aging is not to focus on taking care of the skin, the layer of 2mm. There are several levels of anti-aging of the skin, from the outside to the inside are the epidermis, the dermis, the fat layer, the fascia layer, the muscle layer and the bones, from which you can see the 2mm layer of skin is not the most important, cause anti-aging,the first step is to strengthen the bones, followed by muscle development, then the fascia without inflammation, followed by fat full, and finally the skin is moisturized collagen-rich, so we are to help you from the inside out maintenance, we have Chinese herbs to tonify the liver and kidneys to strengthen the muscles and bones, and then there is the TriLift lifting to exercise the muscles, and finally the Meso and M22 IPL photorejuvenation!